12-UML类图
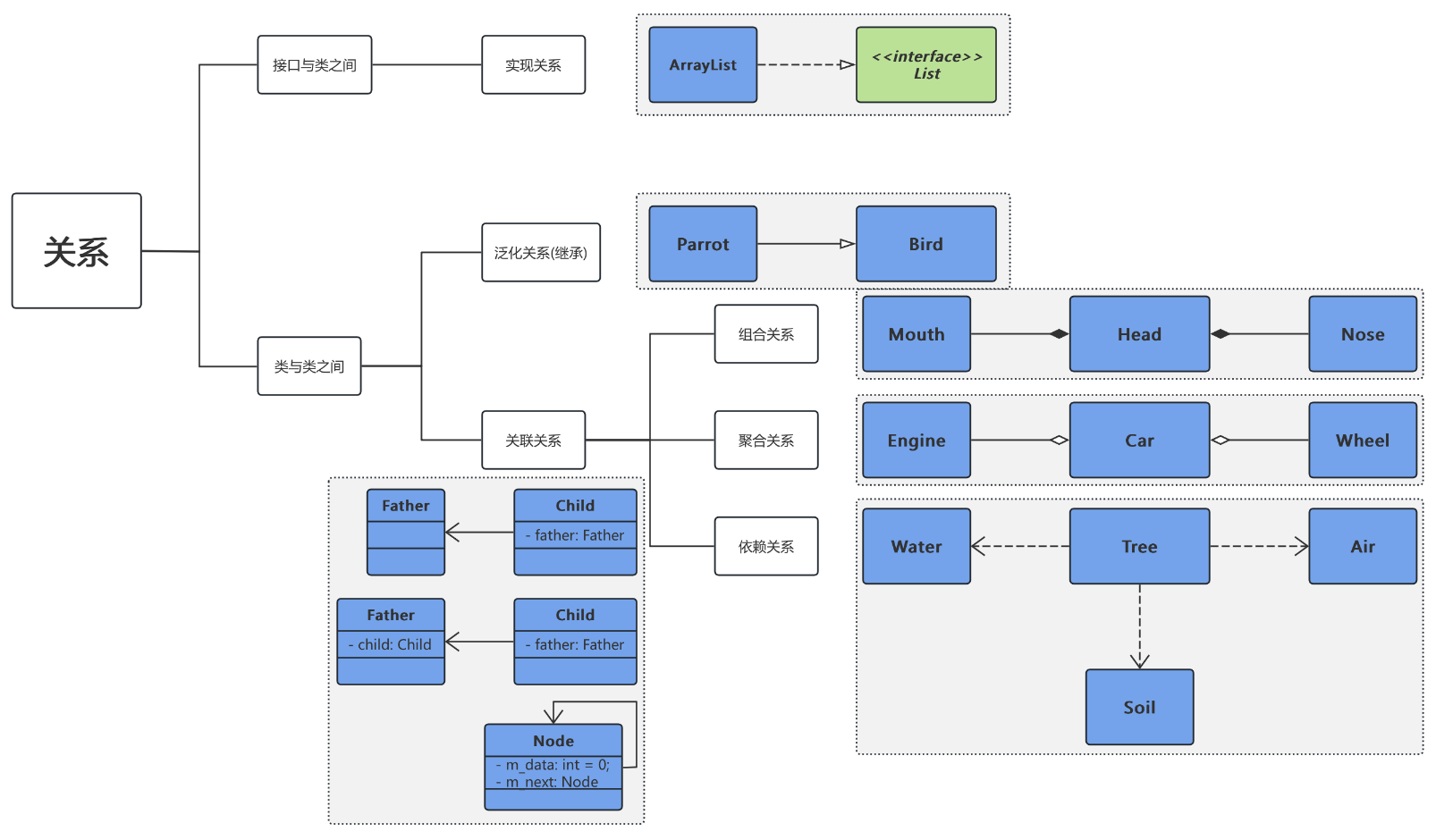
1. 关系
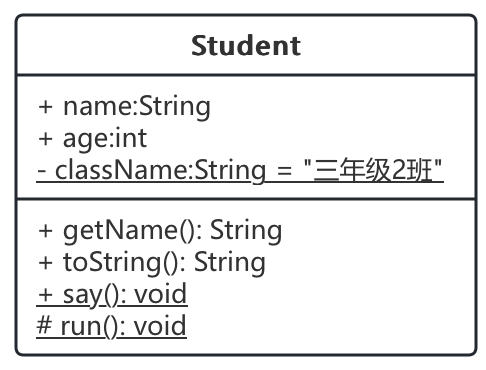
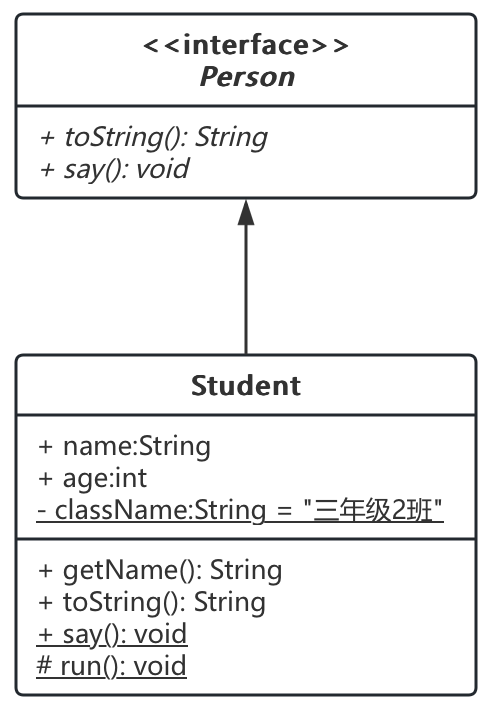
2. 类图
| 可见性 | 符号 | 当前类 | 当前包 | 子孙类 | 其他包 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | - | ✅ | |||
| default/package/friendly | 不写/~ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| protected | # | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| public | + | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
- 其他说明:
=: 表示默认值__下划线: 表示stastic- 斜体:表示抽象类,也可以用两个尖括号包裹起来
3. 类与类之间的关系
| 关系 | 说明 | 表示 |
|---|---|---|
| 继承(泛化) | 继承关系,左:子类,右:父类 |  |
| 实现 | 实现关系:左:实现类;右:接口 |  |
| 关联 | 类与类的联结,【被指向方】作为【指向方】的属性 |  |
| 组合 | 整体和部分关系,【被指向方】部分类,【指向方】整体类 |  |
| 聚合 | 整体和部分关系,【被指向方】部分类,【指向方】整体类 |  |
| 依赖 | 使用关系,【被指向方】使用类,【指向方】被使用类 |  |
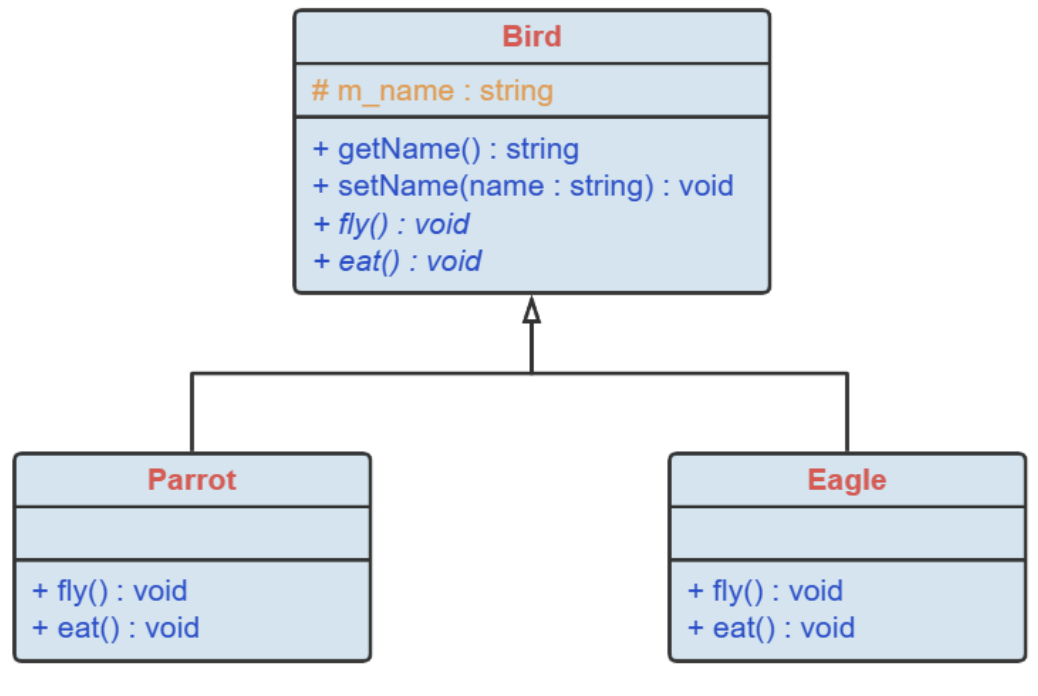
3.1. 泛化关系
- 泛化关系又称为继承关系,父类又称为基类,超类,子类又称为派生类。
- 继承有两种,普通继承,抽象继承
- 两种继承的图形样式一样,都是带空心箭头的实线
3.2. 实现关系
- 比较简单,实现类指向接口
- 图例:
3.3. 关联关系
- 关联关系是最常见的一种关系,它是一种结构化关系,表示一个对象与另一个对象有联系
- 三种:
- 单向关联
- 双向关联
- 自关联
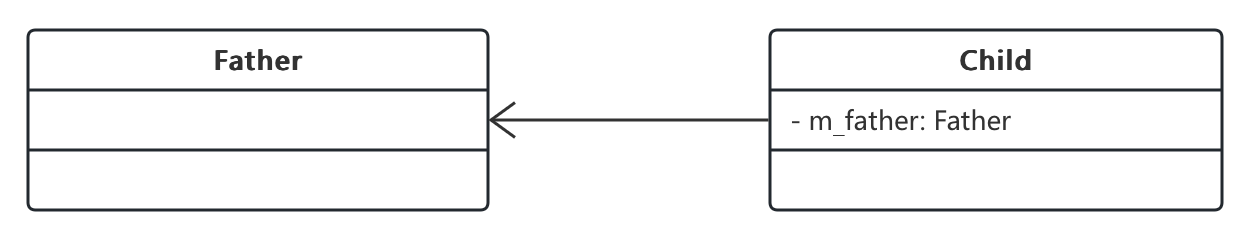
单向关联
- 单向关联指的是关联只有一个方向,比如每个孩子都有一个父亲
class Father {}
class Child {
private Father m_father; // 私有成员变量
}
双向关联
- 每个孩子有有自己的父母,每个父母也有自己的孩子,描述这样的情亲关系:
class Parent {
private Child m_child;
}
class Child {
private Parent m_father; // 私有成员变量
}

有些软件这样表示:
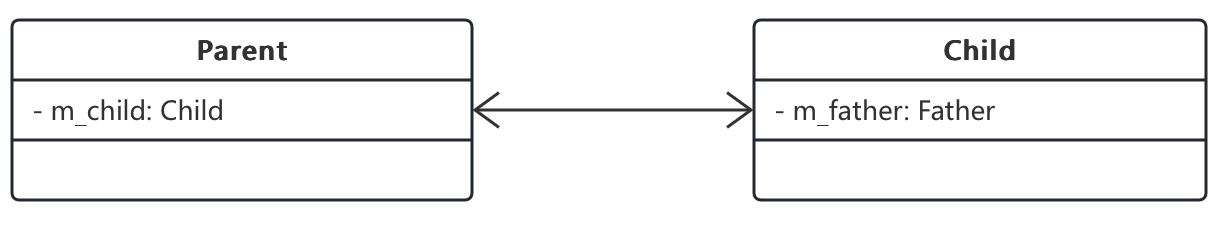
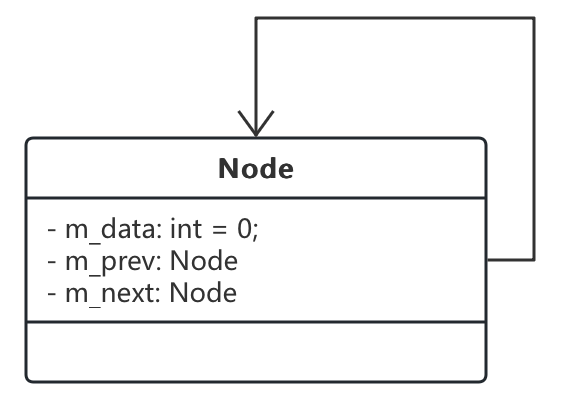
自关联关系
- 自关联关系是指当前类包含一个自身类型的对象成员。这在链表中非常常见,单向链表包含一个,双向链表包含两个;
class Node {
private int m_data = 0;
private Node m_prev = null;
private Node m_next = null;
}
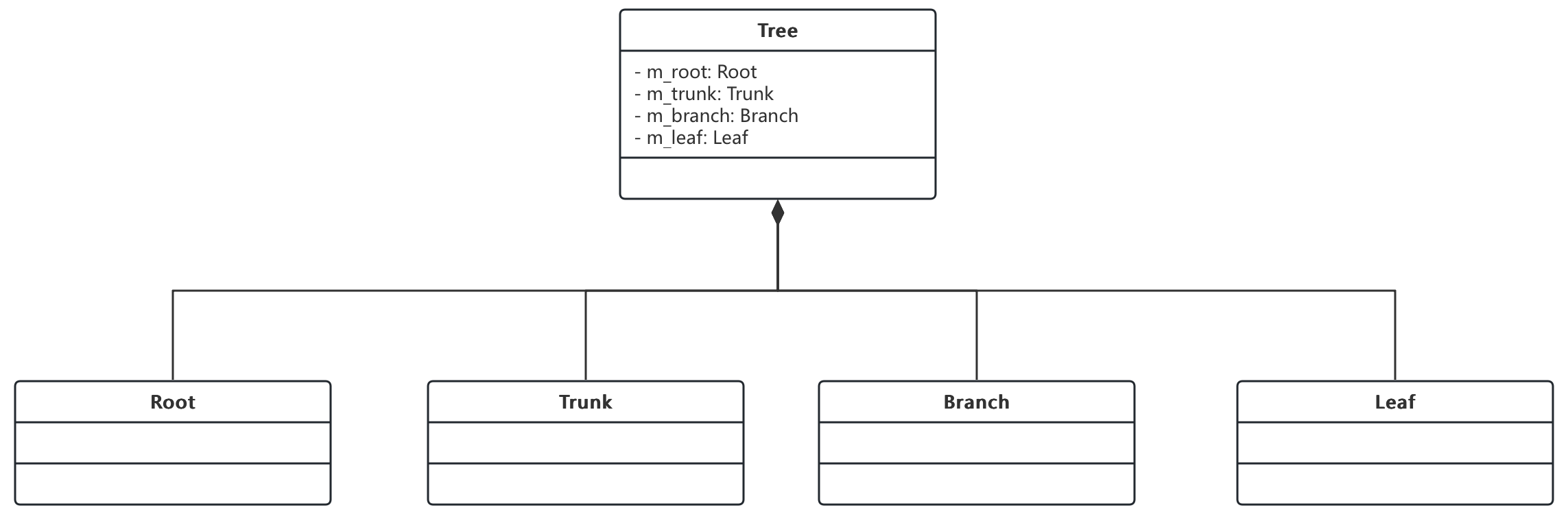
3.4. 组合关系
- 表示整体与部分的关系,但是组合关系中整体对象可以控制成员对象的生命周期,一旦整体对象不存在,成员对象也不存在,整体对象和成员对象之间具有同生共死的关系
- 例子:
- 头(Head) 和嘴巴(Mouth)、鼻子(Nose)、耳朵(Ear)、眼睛(Eye)
- 树(Tree) 和树根(Root)、树干(Trunk)、树枝(Branch)、树叶(Leaf)
- 代码实现(普通版):
class Root {
}
class Trunk {
}
class Branch {
}
class Leaf {
}
class Tree {
private Root m_root;
private Trunk m_trunk;
private Branch m_branch;
private Leaf m_leaf;
public Tree() {
m_root = new Root();
m_trunk = new Trunk();
m_branch = new Branch();
m_leaf = new Leaf();
}
// 不需要写析构函数,Java会自动回收
}
- 代码实现(内部类版):
- 静态内部类,保证无法在外部直接实例化
public class Tree {
private Root m_root;
private Trunk m_trunk;
private Branch m_branch;
private Leaf m_leaf;
public Tree() {
m_root = new Root();
m_trunk = new Trunk();
m_branch = new Branch();
m_leaf = new Leaf();
}
private static class Root {
}
private static class Trunk {
}
private static class Branch {
}
private static class Leaf {
}
}
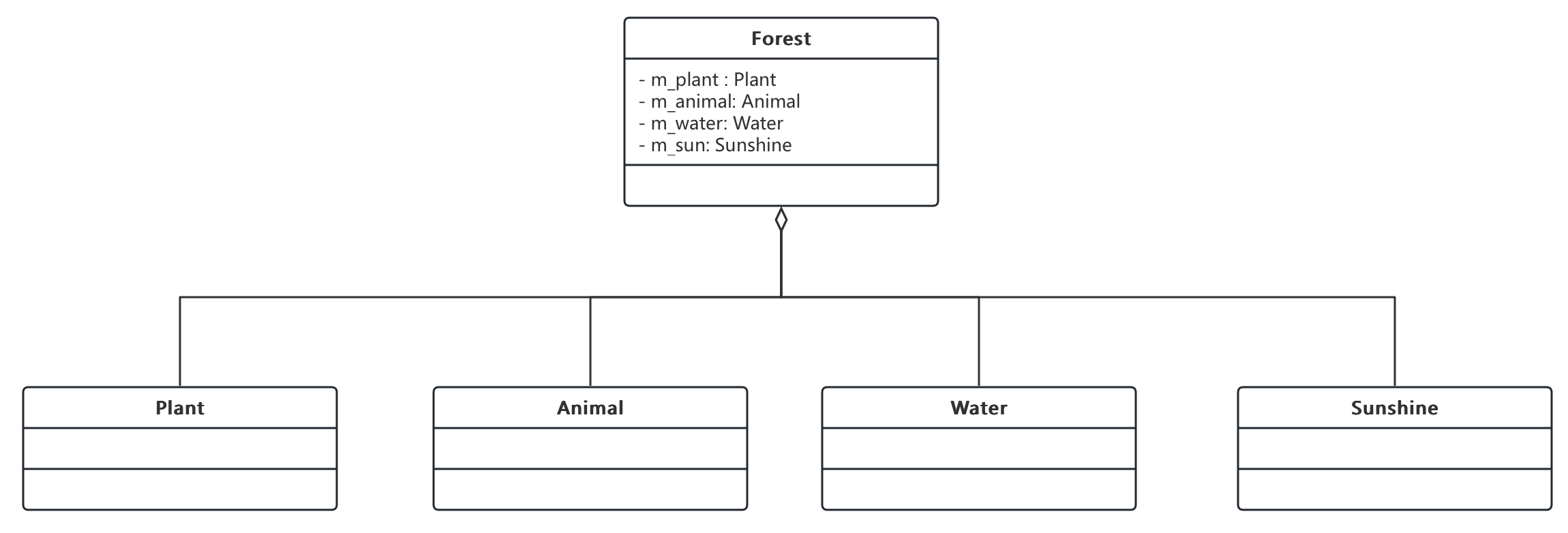
3.5. 聚合关系
- 聚合(Aggregation)关系表示整体与部分的关系,在聚合关系中,成员对象是整体的一部分,但是成员对象可以脱离整体对象独立存在
- 典型例子:
- 汽车(Car) 与引擎(Engine)、轮胎(Wheel)、车灯(Light)
- 森林(Forest) 与植物(Plant)、动物(Animal)、水(Water)、阳光(Sunshine)
// 植物类
class Plant {
// 植物
}
// 动物类
class Animal {
// 动物
}
// 水类
class Water {
// 水
}
// 阳光类
class Sunshine {
// 阳光
}
// 森林类
class Forest {
private Plant plant;
private Animal animal;
private Water water;
private Sunshine sunshine;
public Forest(Plant plant, Animal animal, Water water, Sunshine sunshine) {
this.plant = plant;
this.animal = animal;
this.water = water;
this.sunshine = sunshine;
}
}
3.6. 依赖关系
- 依赖关系是一种使用关系, 在需要表示一个事物使用另一个事物时使用依赖关系。大多数情况下依赖关系体现在某个方法使用另一个类的对象作为参数。
- 实现方式(三种):
- 将一个类的对象作为另一个类中方法的参数
- 在一个类的方法中创建另一个类的对象作为 局部变量
- 在一个类的方法中调用另一个类的静态方法
- 具体例子:
- 驾驶员(
Driver)开车,需要将车(Car)对象作为参数传递给Driver 类的drive()方法。 - 树木(
Tree)的生长,需要将空气(Air)、水(Water)、土壤(Soil)对象作为参数传递给Tree 类的grow()方法。
- 驾驶员(
- 代码示例:
class Car {
public void move() {
// 车辆移动的逻辑
}
}
class Driver {
public void drive(Car car) {
car.move();
}
}
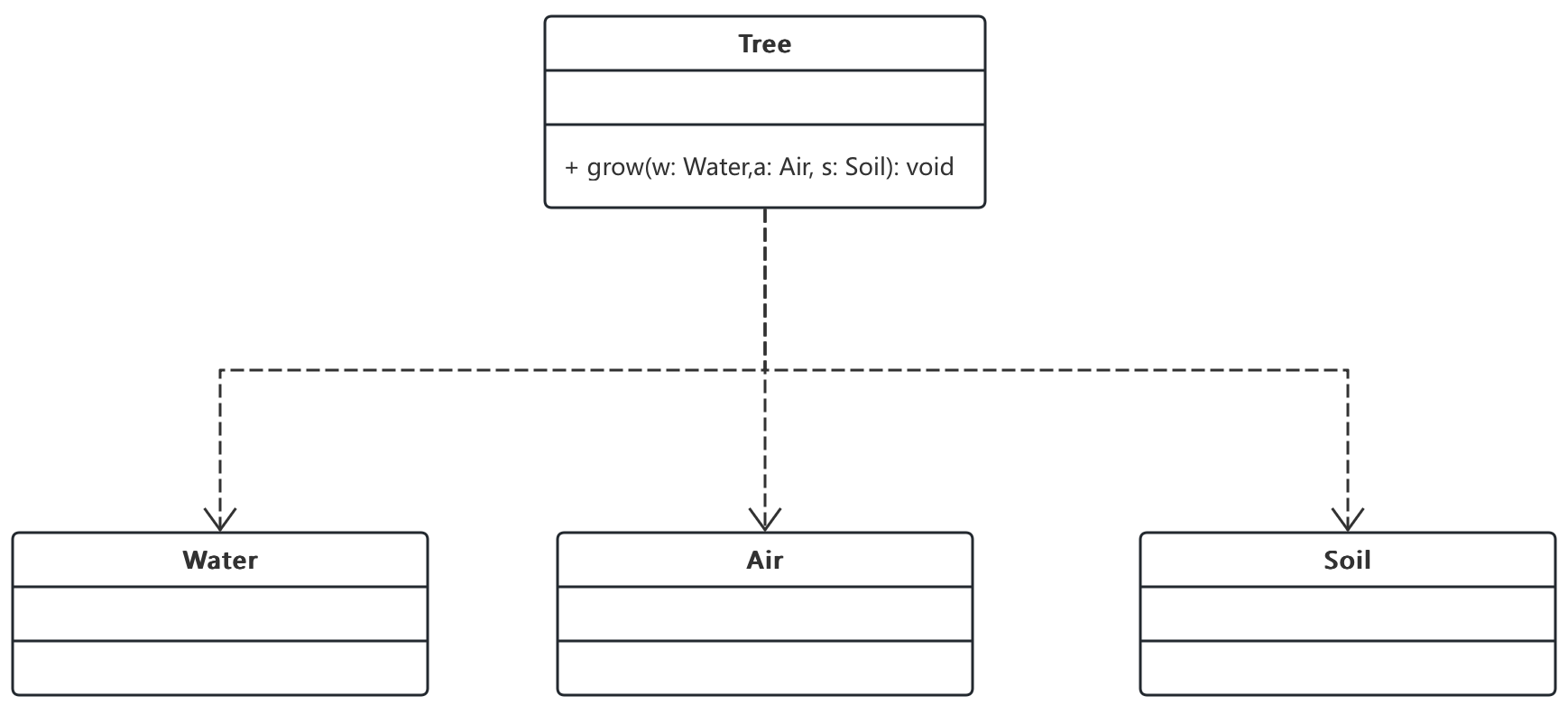
class Water {
// 水的定义
}
class Air {
// 空气的定义
}
class Soil {
// 土壤的定义
}
class Tree {
public void grow(Water w, Air a, Soil s) {
System.out.println("借助 w 中的水分, s 中的养分和 a 中的二氧化碳, 我就可以茁壮成长了");
}
}